39 zero coupon bonds risk
› treasury-bills-vs-bondsTreasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) Bonds are debt instruments also issued by the government or corporate for tenure equal to or more than 2 years period. T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment. › economy › it-rulesIT rules amended to enable infra debt funds to issue zero ... Apr 07, 2022 · The Income Tax department has amended rules to enable infrastructure debt fund and NBFCs to issue zero coupon bonds. Experts say such an amendment will help in mobilisation of resources in a tax ...
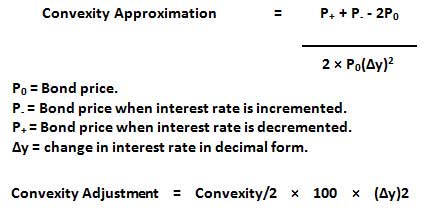
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Like virtually all bonds, zero-coupon bonds are subject to interest-rate risk if you sell before maturity. If interest rates rise, the value of your zero-coupon bond on the secondary market will likely fall. Long-term zeros can be particularly sensitive to changes in interest rates, exposing them to what is known as duration risk.
Zero coupon bonds risk
Zero Coupon Bond - Investor.gov Because zero coupon bonds pay no interest until maturity, their prices fluctuate more than other types of bonds in the secondary market. In addition, although no payments are made on zero coupon bonds until they mature, investors may still have to pay federal, state, and local income tax on the imputed or "phantom" interest that accrues each year. 6.2.1 Flashcards - Quizlet A risk-free, zero-coupon bond has 15 years to maturity. Which of the following is closest to the price per $1000 of face value that the bond will trade at if the YTM is 6.1%? A) $663.78 Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... They are safe investment instruments, and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are said to be the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, in case of longer time duration (a higher 'N'), it might prove to be profitable for the bond holder. Disadvantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds
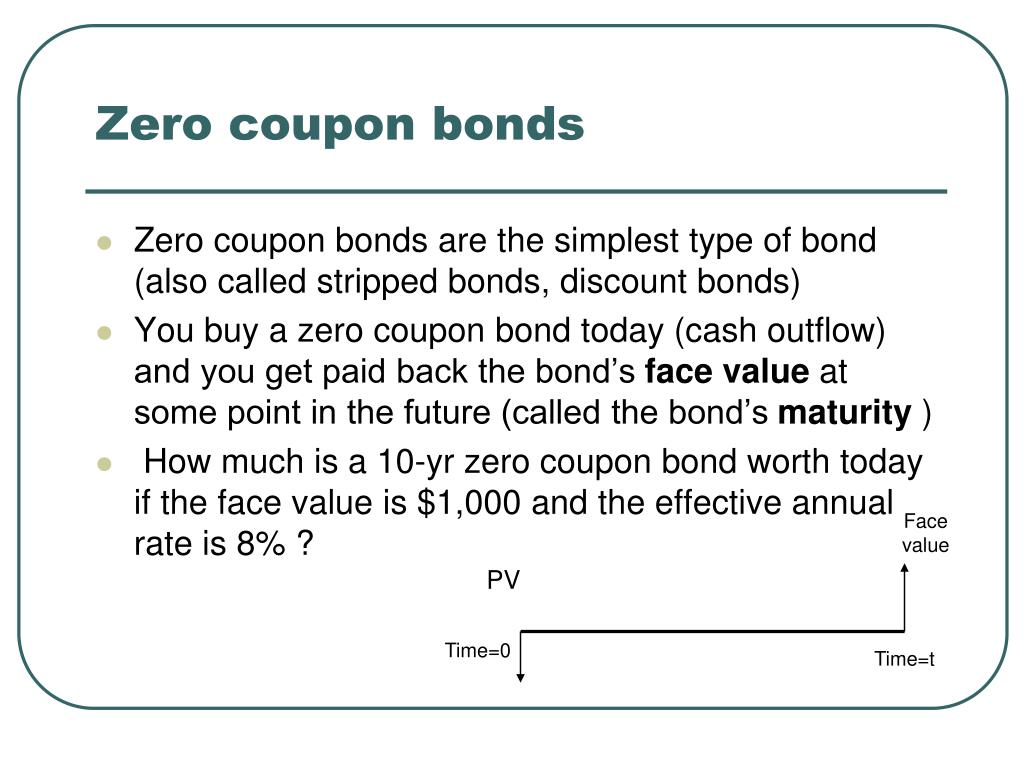
Zero coupon bonds risk. How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price | Double Entry ... The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816) Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds. Understanding Zero-Coupon Bonds As a zero-coupon bond does not pay periodic coupons, the bond trades at a discount to its face value. Zero-Coupon Bonds : What is Zero Coupon Bond? - Groww No reinvestment risk: Other coupon bonds don't allow investors to a bond's cash flow at the same rate as the investment's required rate of returns. But the Zero Coupon bonds remove the reinvestment risk. Zero Coupon bonds do not allow any periodic coupon payments and thus a fixed interest on Zero Coupon bonds is assured. Assessing Risk - Investing In Bonds Market Risk As with all fixed-income securities, the yields or interest rates on zero coupon municipal bonds fluctuate, usually in step with general market rates. While the interest on a bond is fixed by the price you paid, newer bond issues may be offered at higher or lower rates depending on prevailing interest rates when they are issued.
The Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds The Pros and Cons of Zero-Coupon Bonds. Zero-coupon bonds are a type of bond that does not pay any regular interest payments to the investor. Instead, you purchase the bond for a discount and then when it matures, you can get back the face value of the bond. This is a long-term type of investment that can provide nice yields. Characteristics of Zero Coupon Municipal Bonds Zero coupon municipal bonds provide investors with the opportunity to lock in a particular rate of return, without having to worry about reinvestment risk or interest rates in the future. Investors in securities that pay interest semiannually may not always achieve a total realized compounded yield equal to the quoted yield to maturity they ... calculator.me › savings › zero-coupon-bondsZero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to ... In a falling rate envirnoment zero-coupon bonds appreciate much faster than other bonds which have periodic coupon payments. Bonds with a longer duration are more sensitive to the impact of interest rate shifts. Economist Gary Shilling mentioned holders of 30-year zero-coupon bonds purchased in the early 1980s outperformed the S&P 500 with ... › different-kinds-of-bondsTypes Of Bonds: 7 Types Of Financial Bonds For [2022] Oct 28, 2021 · Zero-coupon bonds are one type of bond, while other different types include U.S. Treasuries, agency and municipal bonds, investment-grade and junk bonds, foreign bonds, and convertible bonds. There are government bonds, corporate bonds, and savings bonds.
Zero Coupon Bond - WallStreetMojo Zero-Coupon Bond (Also known as Pure Discount Bond or Accrual Bond) refers to those bonds which are issued at a discount to its par value and makes no periodic interest payment, unlike a normal coupon-bearing bond. In other words, its annual implied interest payment is included in its face value which is paid at the maturity of such bond. Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... They are safe investment instruments, and have a lower element of risk involved. Long Dated zero coupon bonds are said to be the most responsive to interest rate fluctuations. Therefore, in case of longer time duration (a higher 'N'), it might prove to be profitable for the bond holder. Disadvantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds 6.2.1 Flashcards - Quizlet A risk-free, zero-coupon bond has 15 years to maturity. Which of the following is closest to the price per $1000 of face value that the bond will trade at if the YTM is 6.1%? A) $663.78 Zero Coupon Bond - Investor.gov Because zero coupon bonds pay no interest until maturity, their prices fluctuate more than other types of bonds in the secondary market. In addition, although no payments are made on zero coupon bonds until they mature, investors may still have to pay federal, state, and local income tax on the imputed or "phantom" interest that accrues each year.
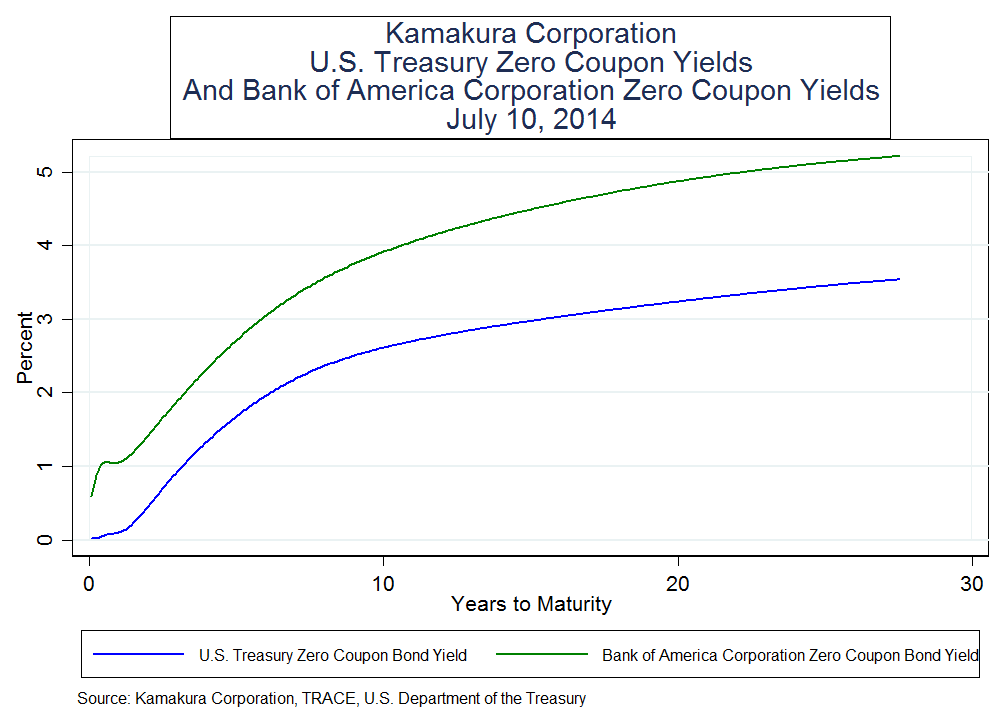
Bank Of America Zero Coupon Bond Yields And Credit Spreads, July 10, 2014 - Donald van Deventer ...

united states - Can zero-coupon bonds go down in price? - Personal Finance & Money Stack Exchange
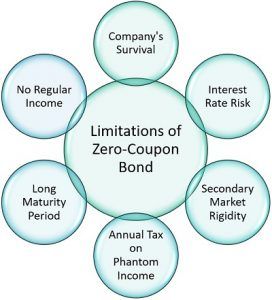
What is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Features, Advantages, Calculation, Example, Limitations ...

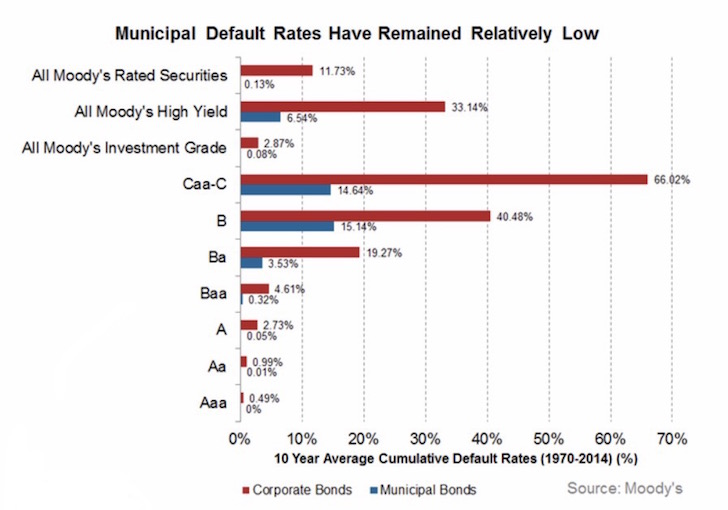
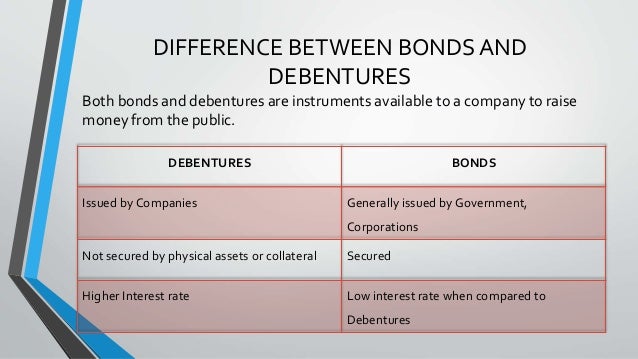



Post a Comment for "39 zero coupon bonds risk"